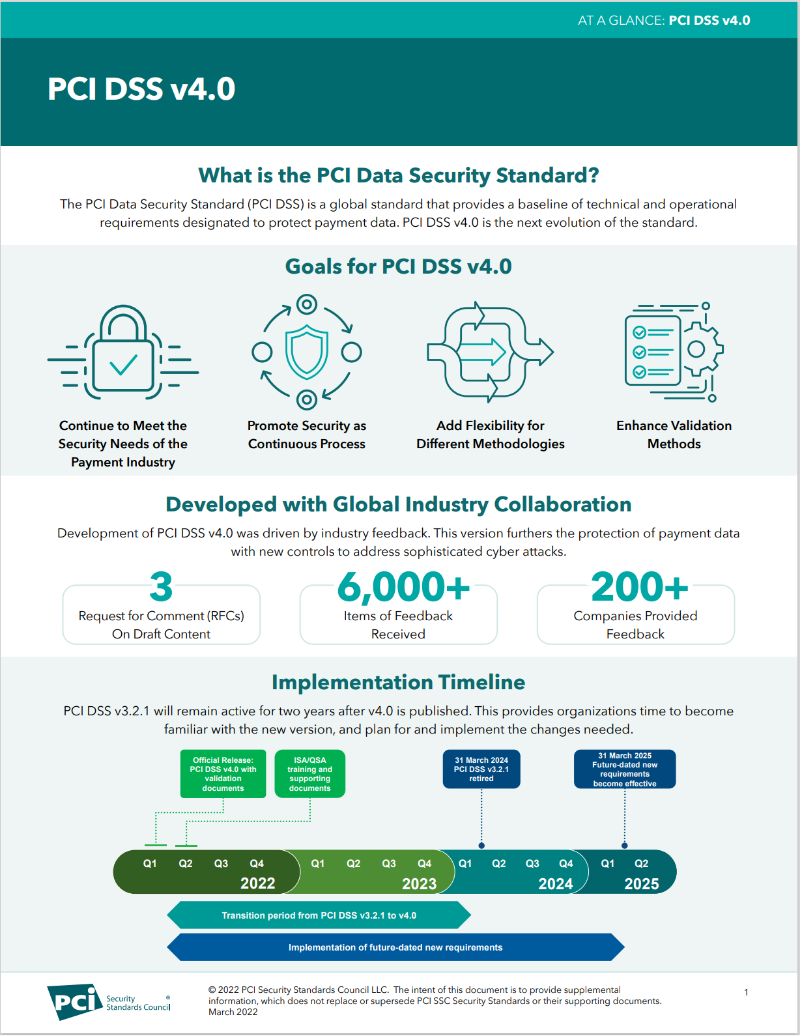
PCI DSS 4.0 is Here - What’s New & What Does it Mean for Your Organisation?
In March this year, the Payment Cards Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) has introduced the new PCI DSS: Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. This initiated the transition from PCI DSS 3.2.1 to the new PCI DSS 4.0.
What is new in PCI DSS v4.0?
The PCI Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a set of security requirements designed to protect cardholder data. PCI DSS v4.0 was released in March 2022 and includes a number of new requirements and changes to existing requirements.
Here are some of the key changes in PCI DSS v4.0:
- Stronger authentication requirements: PCI DSS v4.0 mandates that multi-factor authentication (MFA) must be used for all accounts that have access to cardholder data, not just administrators accessing the CDE.
- Enhanced risk assessment and management: PCI DSS v4.0 requires organisations to conduct a more comprehensive risk assessment and develop a risk management plan that addresses the specific risks to their organisation.
- Increased focus on software security: PCI DSS v4.0 includes new requirements for software security, such as requiring organisations to use secure coding practices and to implement security controls for software development and deployment.
- New requirements for cloud computing: PCI DSS v4.0 includes new requirements for organisations that store cardholder data in the cloud. These requirements address the unique security challenges of cloud computing, such as the shared responsibility model and the need for strong access controls.
In addition to these new requirements, PCI DSS v4.0 also includes a number of changes to existing requirements. For example, the requirement for vulnerability scanning has been updated to reflect the latest security best practices.
What is the timeline for transition to PCI DSS v4.0?
The current version of PCI DSS, v3.2.1, will remain active until it is retired on 31 March 2024. The transition period for organisations to update their PCI DSS Compliance extends to March 31, 2025, but CTOs and cyber security managers are already devoting time and resources to addressing the new PCI DSS requirements.
PCI DSS 4.0 has three main transition categories:
- evolving security requirements,
- clarifications of guidance, and
- structural changes to the regulatory format.
Greater flexibility in PCI DSS v4.0
Version 4 of the PCI DSS ushers in a more customisable approach to regulatory language and specifications, allowing more interpretive scope and implementation flexibility.
Stronger authentication rules in PCI DSS v4.0
PCI DSS v4 achieves closer alignment to the NIST – National Institute of Standards and Technology – cyber security framework in its guidance on MFA and passwords.
These changes in PCI DSS 4.0 are worth a close look
Let’s take a look at some of the most significant changes in PCI DSS 4.0 in terms of PCI DSS best practice for retailers, merchants and the cyber security industry.
There’s a newly introduced customisable approach to implementation in PCI DSS 4.0. For certain requirements, retailers and service providers can propose any alternative control measures that meet the objectives of the PCI rules. This latitude gives compliant organisations some flexibility in achieving the goals set out in the PCI standards, allowing greater efficiency and the opportunity to create more unique perimeters. The new flexibility in PCI DSS v4 encourages the creation of stronger perimeter defences because greater variation across the industry makes it harder for attackers to use copy/paste tactics.
Greater flexibility in the wording of PCI SSC requirements is a significant step forward in future-proofing the standard and helping keep cyber security architectures contemporary. The threat landscape changes fast, so regulatory focus on outcomes rather than specific architectures or technologies makes it easier for organisations and their Managed Security Service Providers (MSSP) to mount effective, timely defences.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is mandatory across all key systems covered by the regulations, and PCI DSS 4.0 mandates longer password lengths for all compliant authentication profiles. In addition, the former requirement to change passwords every 90 days can be removed in certain circumstances. Additional control measures, such as checking passwords against a list of known bad passwords, have also been introduced to the standard.
How to transition from PCI DSS 3.2.1 to PCI DSS 4.0
The transition to PCI DSS 4.0 involves 65 requirements, 54 covering all entities and 11 pertaining to service providers only.
- 14 measures are immediately applicable to all version 4.0 assessments.
- Multiple roles and responsibilities clauses are included for each requirement.
- Requirement clause 12.3.2 mandates a risk analysis that follows a repeatable and robust methodology enabling the achievement of a “customised approach.”
- Requirement 12.5.2 demands frequent validation of PCI DSS scope with the aim of ensuring it stays up to date and is consistently aligned with changing organisational objectives.
- Requirement 12.9.2 deals with documentation demonstrating the maintenance of proper security around customer data. In conjunction with Requirement 12.9.1, this clause seeks to establish a unilateral understanding of PCI DSS responsibilities.
- There are 51 future requirements specified in PCI DSS 4.0, which are deemed best practice until March 31 2025.
How can Sekuro help you manage your transition to PCI DSS 4.0?
Sekuro is an officially recognised Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) company authorised by the PCI SSC to review organisations’ compliance. As such, we’re certified to validate the adherence of payment software systems to the PCI DSS.
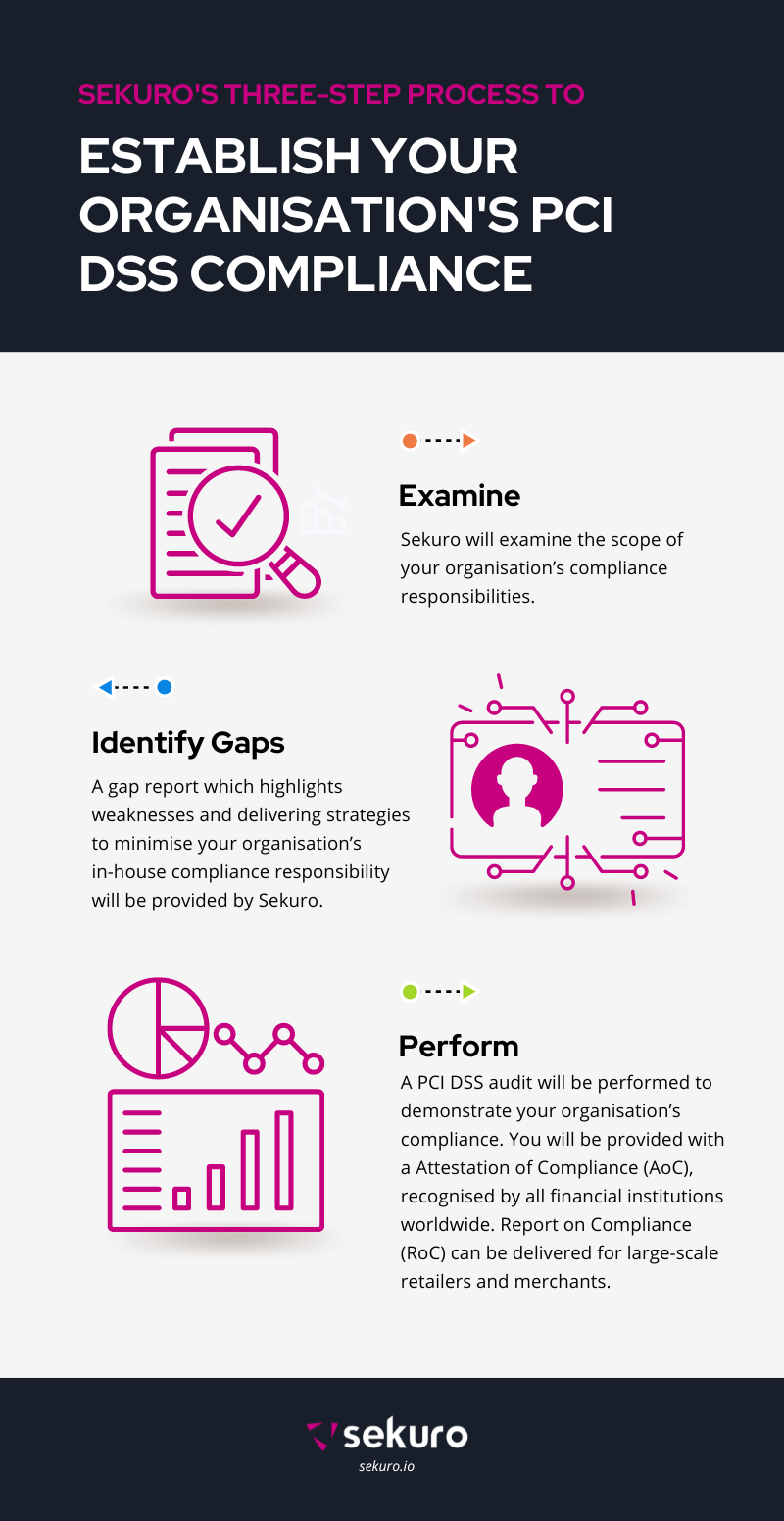
Sekuro conducts a three-stage process to establish our customers’ PCI DSS compliance.
- We examine what’s in the scope of your organisation’s compliance responsibilities, identifying any points where your customers’ data is captured as part of the card-handling process.
- Once we’ve identified the gaps in a client’s compliance that can lead to a vulnerability issue, we provide them with a gap report highlighting weaknesses and delivering strategies to minimise the organisation’s in-house compliance responsibility. Sekuro offers ongoing security support and remediation with MSSP services and third-party technology automation.
- To satisfy the requirements of the PCI SSC, we perform a PCI DSS audit to demonstrate your organisation’s compliance. Sekuro will provide you with an Attestation of Compliance (AoC) recognised by all financial institutions worldwide.
For the largest-scale retailers and merchants, Sekuro can deliver an Report on Compliance (RoC). The PCI DSS mandates that RoCs must be performed by a Qualified Security Auditor Company such as Sekuro.
As an experienced and dependable MSSP, Sekuro has a track record of helping our clients navigate their responsibilities under the PCI DSS. We offer:
- PCI DSS compliance consulting
- comprehensive MSSP advisory services
- personnel services in team augmentation and recruiting
- security vendor partnership services
You can read our case study “PCI- DSS Assessment With Reap: Protecting Card Holder Data For A Next-Gen Digital Payments Platform” to learn more about how we help our clients meet their PCI DSS compliance responsibilities.
What is PCI DSS?
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a global cyber security compliance standard affecting retailers both online and in the brick-and-mortar realm.
Let’s briefly review the significance of the regulations for merchants and the cyber security industry:
- The PCI DSS requirements are defined by the Payment Cards Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) which seeks to provide consistency and confidence for merchants and financial institutions.
- The PCI DSS is designed to protect sensitive cardholder data processed or captured by merchants or organisations handling payment cards such as Visa, Amex, Mastercard, etc.
- PCI DSS compliance is enforced through contracts between card payment brands and acquiring banks. Any entity handling cardholder data is required to be PCI DSS compliant. Additionally, organisations offering services to customers where the security of PCI DSS-compliant data is affected must also be PCI DSS compliant.
- Key cyber security requirements governed by the PCI DSS rules include:
- multi-factor authentication
- levels of transaction encryption
- vulnerability testing
PCI DSS 4.0 FAQ
What organisations have to comply with the PCI standards?
Each of PCI SSC’s Participating Payment Brand members (American Express, Discover, JCB International, Mastercard, UnionPay, and Visa) currently have their own PCI compliance programs for the protection of their affiliated payment card account data. Any merchant, SME or corporation handling cardholder data must be PCI DSS compliant.
What software is subject to validation under the PCI Secure Software Standard?
The eligibility criteria for software validation to the PCI Secure Software Standard is defined in the Secure Software Program Guide, available in the PCI SSC Document Library. Whether an entity is required to use software validated to the Secure Software Standard is determined by individual payment brand mandates and not by PCI SSC.
How can I ensure that my organisation is PCI DSS 4.0 compliant?
PCI DSS 4.0 compliance can be complex, so it’s advisable to get a comprehensive gap assessment from a qualified consultant.
How do I get started with PCI DSS?

Gus Davison
OffSec Sales SME, Sekuro
Gus is an experienced OffSec Sales SME at Sekuro. Gus has worked with many organisations to asses their OffeSec needs in order understand our customers requirements and business, ensuring to build a market leading approach that protects business resilience.







